Understanding the distinction between the internet and networks is essential in today’s digital age, where connectivity is vital for both personal and professional interactions. These concepts often get confused, leading to misconceptions about how devices communicate and share information. This article aims to clarify the differences and enhance your digital literacy.
Defining the Internet
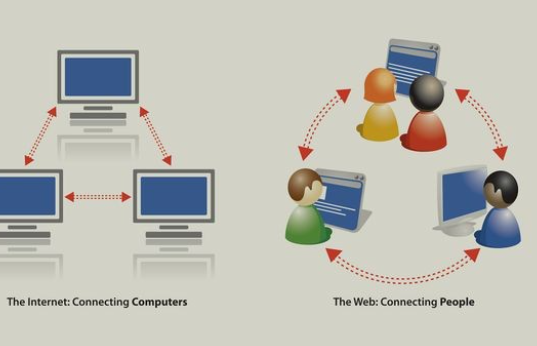
The internet is a vast global network that connects millions of private, public, academic, business, and government networks. It enables diverse forms of communication, including browsing websites, sending emails, and streaming media. Essentially, the internet serves as the backbone infrastructure that supports various services and applications, allowing data to flow seamlessly across the globe.
Understanding Networks
A network, on the other hand, is a collection of computers and devices interconnected to share resources and information. Local Area Networks (LANs) and Wide Area Networks (WANs) are common types of networks. While the internet is an expansive collection of interconnected networks, a network can exist independently without being connected to the internet, such as a home network where devices can share files and printers without external access.
Key Differences
The primary difference between the internet and a network lies in their scope and function. The internet is a global system designed to facilitate communication between various networks, while a network serves a specific purpose, whether local or regional. Additionally, networks can operate without the internet, but the internet cannot function without interconnected networks to support its infrastructure.
In summary, while both the internet and networks play vital roles in our digital lives, understanding their differences is crucial for effective communication and technology use. Delve deeper into this topic to better harness technology for your needs or explore further advancements in connectivity.